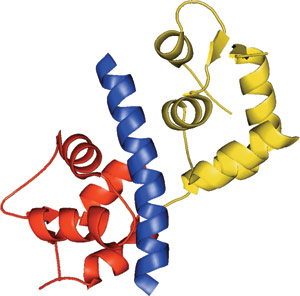
The IQ motif of Myo2p bound to Mlc1p N-lobe (red) and C-lobe (yellow).
The IQ domain is approximately 25 amino acids in length and is widely distributed in nature. The motif conforms to the consensus sequence [I,L,V]QxxxRGxxx[R,K], which forms an amphiphilic seven-turn α-helix capable of binding calmodulin in a Ca2+-independent manner. IQ motifs result in either compact or extended light chain conformations. Calmodulin mediates the effects of the major cellular second signal Ca2+ and can stimulate changes in the actin cytoskeleton mediated by proteins such as myosin. Nearly all myosin proteins possess between one and seven IQ domains, most found in multiple tandem repeats separated by 9-16 amino acid residues. Binding of calmodulin by IQ motifs from a diverse set of proteins might allow Ca2+ signaling to effect a wide range of cellular activities. Proteins that contain at least one IQ domain include myosin, voltage-operated channels, neuronal growth proteins, phosphatases, sperm surface proteins, Ras exchange proteins, spindle-associated proteins, at least one RasGAP-like protein and several plant-specific proteins.
The IQ domain forms an uninterrupted seven-turn α-helix that is distinctly amphiphilic. The non-polar face of the helix switches sides after the fifth turn, providing an additional surface for ligand contact. Residues important for interactions with calmodulin include a hydrophobic amino acid at position 1, a highly conserved glutamine at position 2, basic charges at positions 6 and 11, and a variable glycine at position 7. Substitution of this glycine at position 7 with residues containing bulky side chains, which occurs in approximately 50% of IQ domains, may provide some specificity for calmodulin interactions. The identity of the six intervening amino acids in the IQ consensus sequence may be involved with calmodulin specificity.
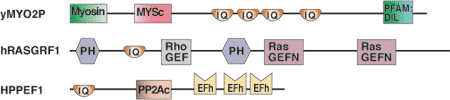
| IQ Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
| Myo2p (class V myosin) | Mlc1p (calmodulin-like myosin light chain), Ca2+-independent |
| Neurogranin | CaM (calmodulin), Ca2+-independent and regulated by PKC phosphorylation of the IQ motif |
| Ras-GRF (exchange factor) | CaM (calmodulin), Ca2+-induced binding to IQ domain |