Revision 13
#87105
Store at +4C
PathScan® RP Total Vimentin Sandwich ELISA Kit
1 Kit
(96 assays)
Species Cross Reactivity:
H Mk
UniProt ID:
#P08670
Entrez-Gene Id:
#7431
877-616-CELL (2355)
877-678-TECH (8324)
3 Trask Lane | Danvers | Massachusetts | 01923 | USA
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
| Product Includes | Product # | Quantity | Color | Storage Temp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vimentin Rabbit mAb Coated Microwells | 95256 | 96 tests | +4C | |
| Vimentin Mouse Detection mAb | 15464 | 1 ea | Red (Lyophilized) | +4C |
| HRP Diluent | 13515 | 5.5 ml | Red | +4C |
| TMB Substrate | 7004 | 11 ml | +4C | |
| STOP Solution | 7002 | 11 ml | +4C | |
| Sealing Tape | 54503 | 2 ea | +4C | |
| ELISA Wash Buffer (20X) | 9801 | 25 ml | +4C | |
| Cell Lysis Buffer (10X) | 9803 | 15 ml | -20C |
Kit contents scale proportionally with size, except sealing tape.
Example: The V1 kit contains 5X the listed quantities above, but will exclude the sealing tape.
For the “C” and “V” kits, the supplied 96-well strip plate consists of twelve 8-well strips in a support frame. This enables custom plate configurations.
Description
*Antibodies in this kit are custom formulations specific to the kit.
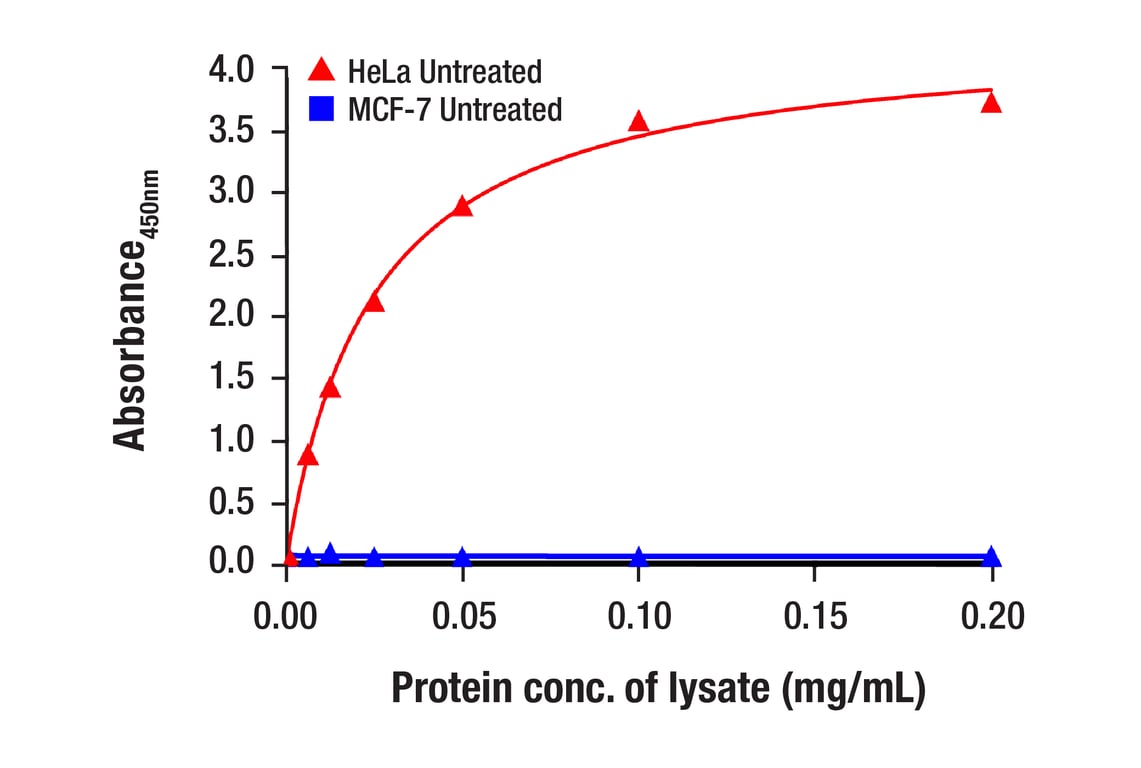
Specificity/Sensitivity
Background
During mitosis, CDK1 phosphorylates vimentin at Ser56. This phosphorylation provides a PLK binding site for vimentin-PLK interaction. PLK further phosphorylates vimentin at Ser83, which might serve as a memory phosphorylation site and play a regulatory role in vimentin filament disassembly (8,9). Additionally, studies using various soft-tissue sarcoma cells have shown that phosphorylation of vimentin at Ser39 by Akt1 enhances cell migration and survival, suggesting that vimentin could be a potential target for soft-tissue sarcoma targeted therapy (10,11).
Background References
- Eng, L.F. et al. (2000) Neurochem Res 25, 1439-51.
- Goebel, H.H. et al. (1987) Acta Histochem Suppl 34, 81-93.
- Leader, M. et al. (1987) Histopathology 11, 63-72.
- Helfand, B.T. et al. (2004) J Cell Sci 117, 133-41.
- Tang, D.D. et al. (2005) Biochem J 388, 773-83.
- Fomina, I.G. et al. (1990) Klin Med (Mosk) 68, 125-7.
- Nieminen, M. et al. (2006) Nat Cell Biol 8, 156-62.
- Yamaguchi, T. et al. (2005) J Cell Biol 171, 431-6.
- Oguri, T. et al. (2006) Genes Cells 11, 531-40.
- Zhu, Q.S. et al. (2011) Oncogene 30, 457-70.
- Xue, G. and Hemmings, B.A. (2013) J Natl Cancer Inst 105, 393-404.
Trademarks and Patents
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
PathScan is a registered trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
U.S. Patent No. 7,429,487, foreign equivalents, and child patents deriving therefrom.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit cellsignal.com/trademarks for more information.
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.
Revision 13