Revision 1
#14197
Store at -20C
877-616-CELL (2355)
877-678-TECH (8324)
3 Trask Lane | Danvers | Massachusetts | 01923 | USA
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
Applications:
W, IP, IF-IC
Reactivity:
H M R Mk
Sensitivity:
Endogenous
MW (kDa):
180
Source/Isotype:
Rabbit IgG
UniProt ID:
#Q03164
Entrez-Gene Id:
4297
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:50 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:200 |
Storage
Specificity/Sensitivity
Source / Purification
Background
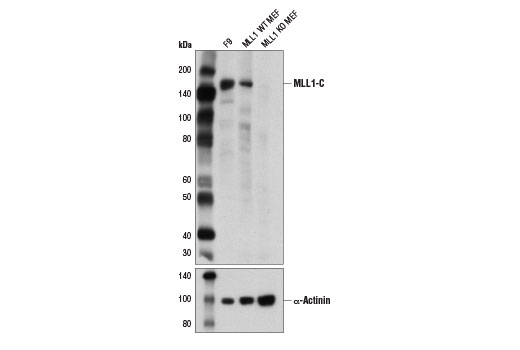
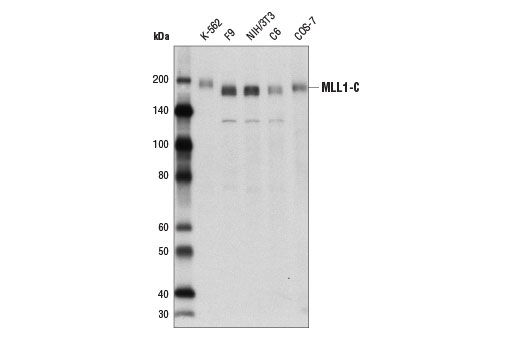
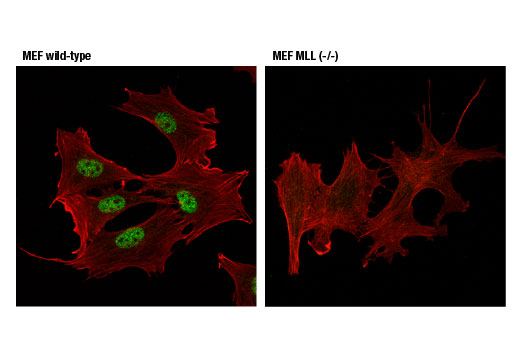
MLL1 functions as a master regulator of both embryogenesis and hematopoiesis, and is required for proper expression of Hox genes (7,8). MLL1 is a large, approximately 4000 amino acid, protein that is cleaved by the taspase 1 threonine endopeptidase to form N-terminal (MLL1-N) and C-terminal MLL1 (MLL1-C) fragments, both of which are subunits of the functional MLL1/COMPASS complex (9,10). MLL1-N, MLL1-C, WDR5, RBBP5 and ASH2L define the core catalytic component of the MLL1/COMPASS complex, which is recruited to target genes and methylates histone H3 lysine 4 to regulate transcriptional initiation (11). At least 60 different MLL1 translocation partners have been molecularly characterized and associated with various hematological malignancies. The most common translocation partners include AF4, AF9, ENL, AF10, ELL and AF6 (8,12,13). With the exception of AF6, all of these partners are nuclear proteins that function to positively regulate transcriptional elongation. AF4, AF9 and ENL are all components of the super elongation complex (SEC), while AF4, AF9, AF10 and ENL all interact with the histone H3 lysine 79 methyltransferase DOT1L. Many MLL1 target genes are normally regulated by promoter-proximal pausing, with the release of RNA polymerase and transcriptional elongation occurring in response to proper stimuli (14). The association of MLL1 translocation partners with SEC and DOT1L suggest that MLL1-fusion proteins may function to sustain specific gene expression programs by constitutively activating transcriptional elongation.
Background References
- Miller, T. et al. (2001) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98, 12902-7.
- Shilatifard, A. (2008) Curr Opin Cell Biol 20, 341-8.
- Tenney, K. and Shilatifard, A. (2005) J Cell Biochem 95, 429-36.
- Lee, J.H. and Skalnik, D.G. (2005) J Biol Chem 280, 41725-31.
- Lee, J.H. et al. (2007) J Biol Chem 282, 13419-28.
- Hughes, C.M. et al. (2004) Mol Cell 13, 587-97.
- Eissenberg, J.C. and Shilatifard, A. (2010) Dev Biol 339, 240-9.
- Smith, E. et al. (2011) Genes Dev 25, 661-72.
- Takeda, S. et al. (2006) Genes Dev 20, 2397-409.
- Yokoyama, A. et al. (2002) Blood 100, 3710-8.
- Dou, Y. et al. (2006) Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 713-9.
- Yip, B.H. and So, C.W. (2013) Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 238, 315-23.
- Neff, T. and Armstrong, S.A. (2013) Blood 121, 4847-53.
- Wang, P. et al. (2009) Mol Cell Biol 29, 6074-85.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
W: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry)
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: Human M: Mouse R: Rat Mk: Monkey
Trademarks and Patents
Cell Signaling Technology is a trademark of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Visit cellsignal.com/trademarks for more information.
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.
Revision 1