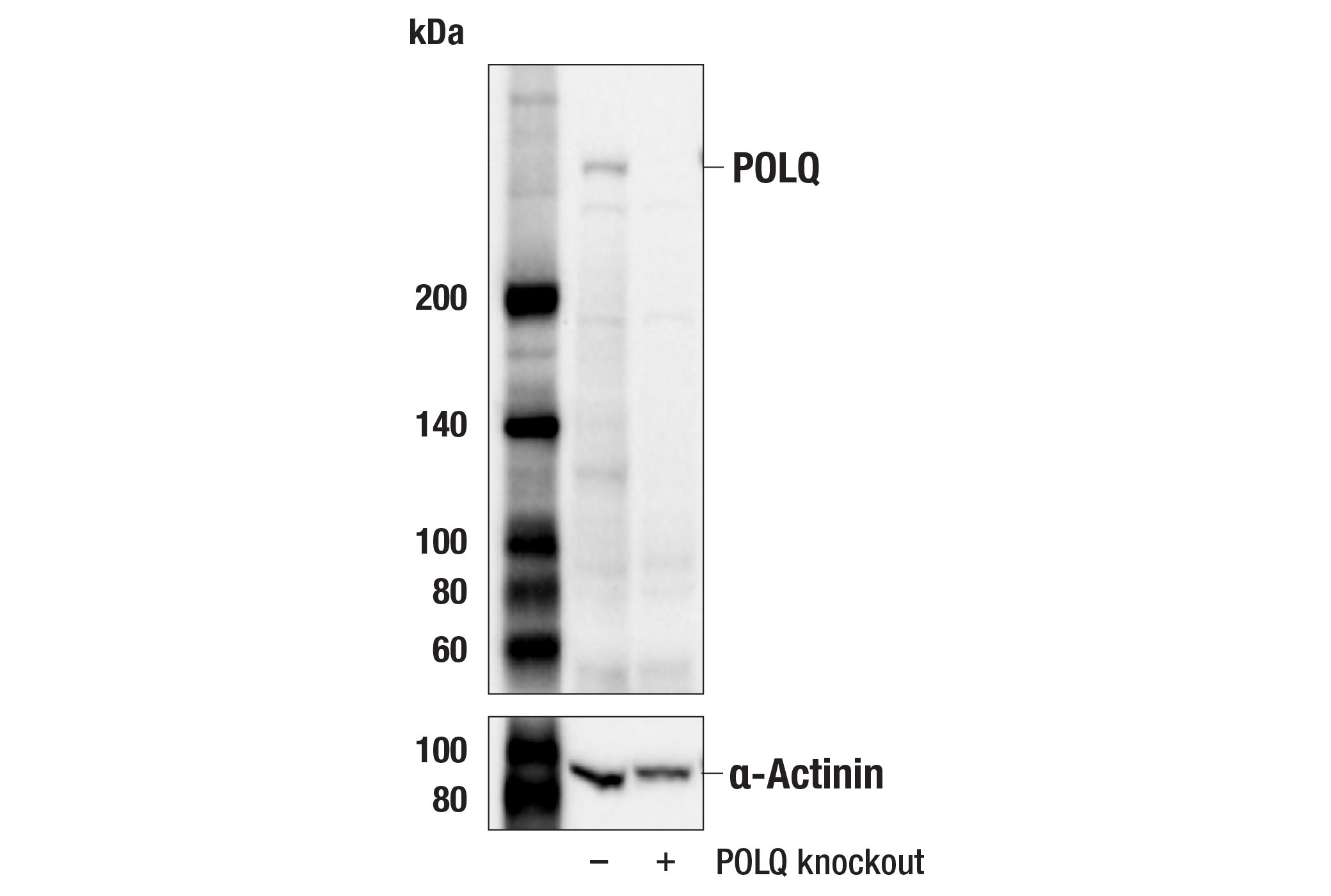
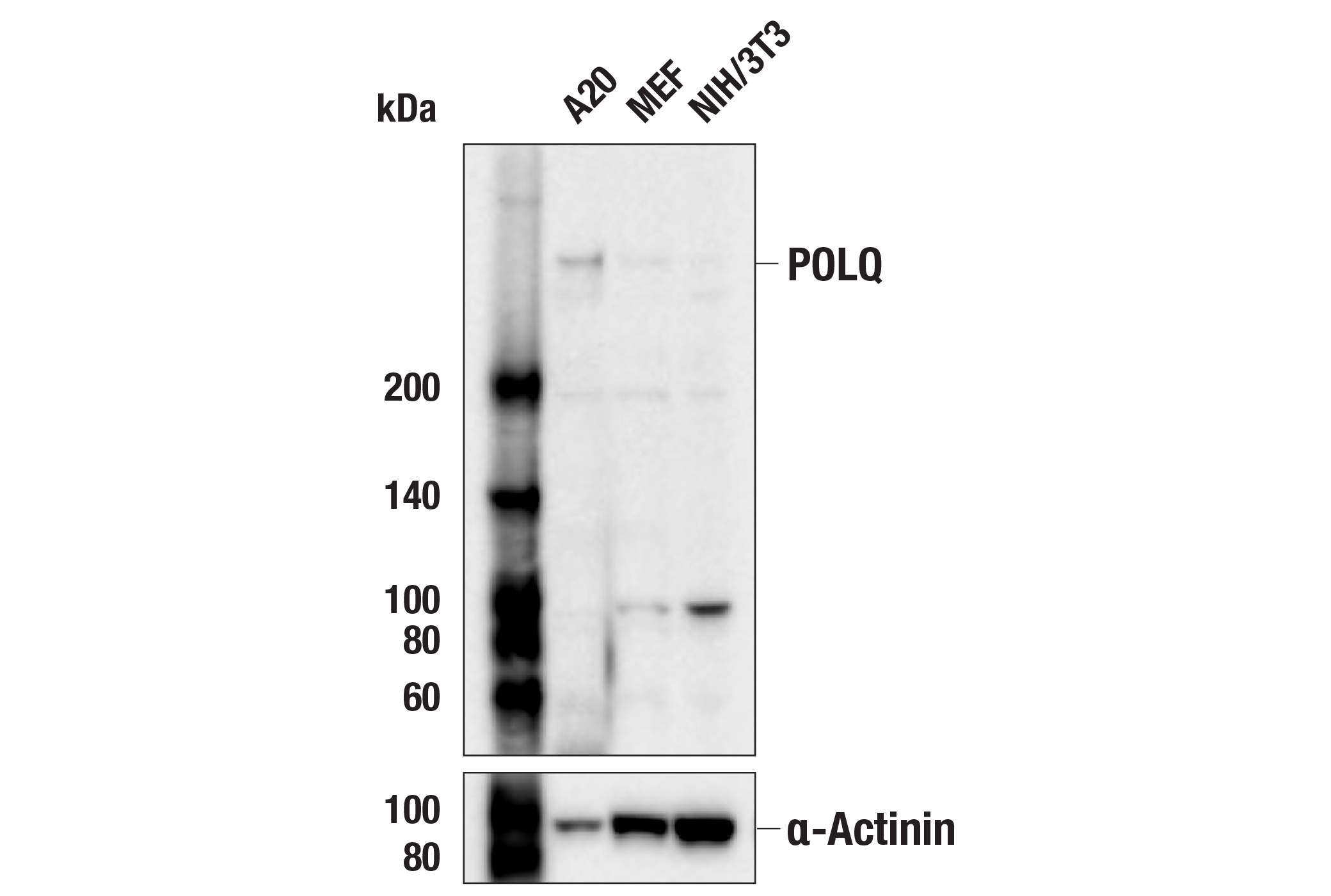
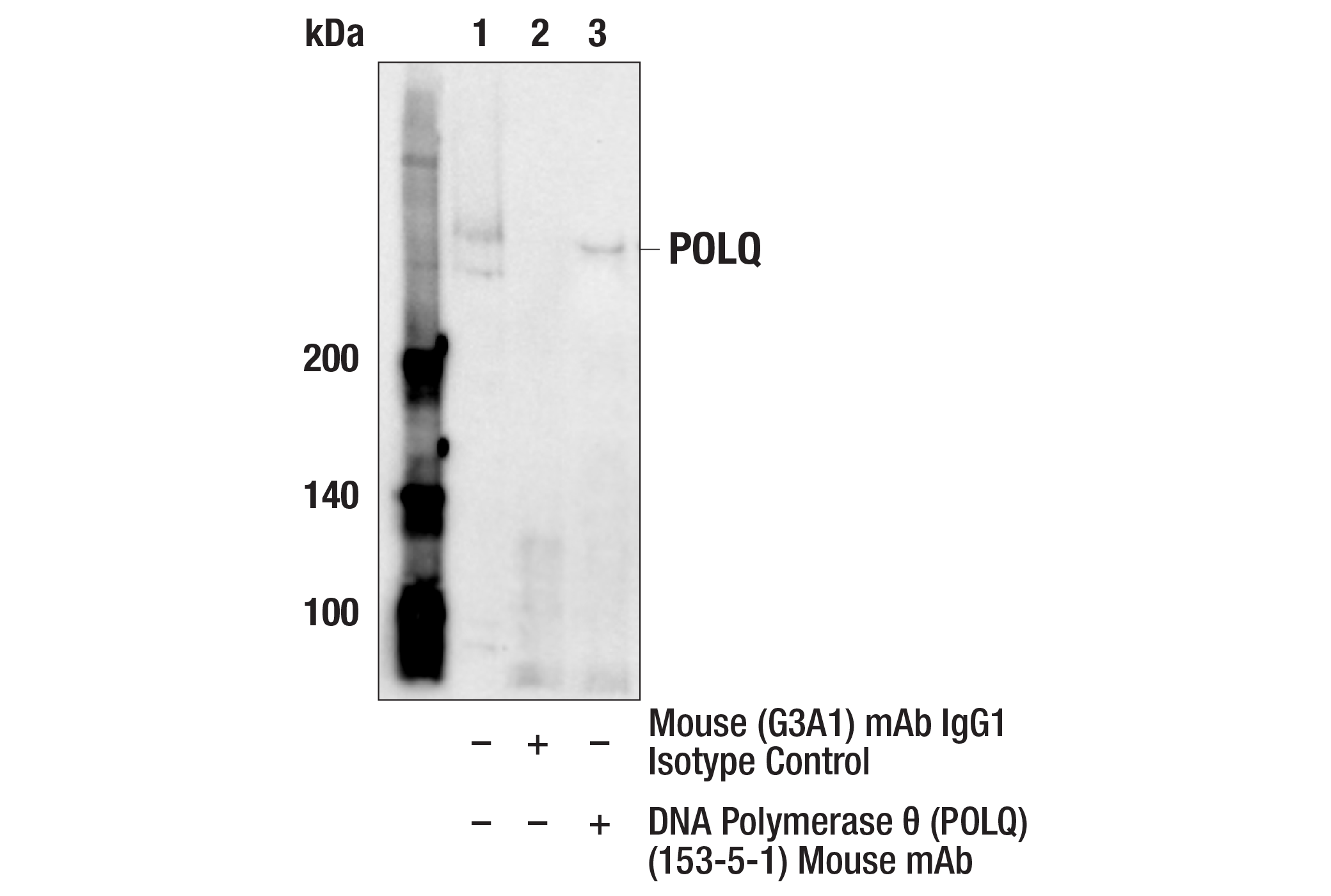
WB, IP
M
Endogenous
280
Mouse IgG1 kappa
#O75417
10721
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:100 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Mouse
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with recombinant protein specific to the carboxy terminus of human POLQ protein.
Background
Mammalian cells undergo DNA damage in response to various intrinsic and extrinsic forces, and signaling pathways are in place to sense and repair damaged DNA to avoid genome instability and mutation. Repair of toxic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) can occur through several pathways, and pathway choice may depend on the cell cycle phase and the nature of the DSB (1). The two main pathways for DSB repair are classical non-homologous end joining (C-NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR). In addition, three error-prone pathways, single-strand annealing (SSA), microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ), and polymerase theta-mediated end-joining (TMEJ) have been described (2).
Exploiting DNA repair deficiencies in human cancer by targeting intact DNA repair pathways is a promising approach to cancer therapy. This approach has been successful with the use of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors in HR-deficient cancer (3).DNA polymerase θ, encoded by the POLQ gene, is a 290 kDa protein with an N-terminal helicase-like domain and a C-terminal DNA polymerase domain (4). ZEB1, an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) transcription factor, has been shown to regulate TMEJ by suppressing POLQ expression (5). DNA polymerase θ is essential in TMEJ and is, therefore, an important target for drug development in HR-deficient cancers (6,7). Several inhibitors of DNA polymerase θ are under investigation in pre-clinical and clinical trials (8,9).
- Li, L.Y. et al. (2020) Front Pharmacol 11, 629266.
- Hanscom, T. and McVey, M. (2020) Cells 9, 1657. doi: 10.3390/cells9071657.
- Mehta, P. and Bothra, S.J. (2021) Adv Genet 108, 35-80.
- Yousefzadeh, M.J. and Wood, R.D. (2013) DNA Repair (Amst) 12, 1-9.
- Prodhomme, M.K. et al. (2021) Cancer Res 81, 1595-1606.
- Wyatt, D.W. et al. (2016) Mol Cell 63, 662-673.
- Brambati, A. et al. (2020) Curr Opin Genet Dev 60, 119-126.
- Ramsden, D.A. et al. (2022) Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 23, 125-140.
- Pismataro, M.C. et al. (2023) J Med Chem 66, 6498-6522.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v nonfat dry milk, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.