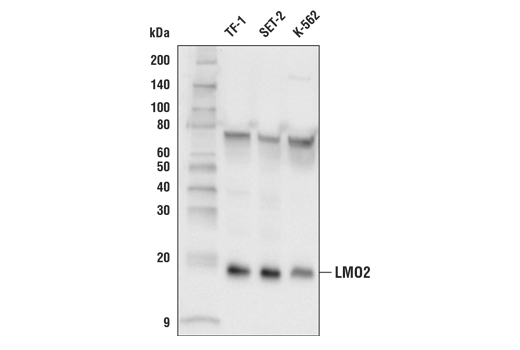
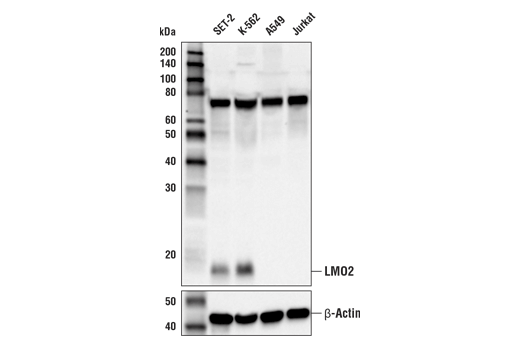
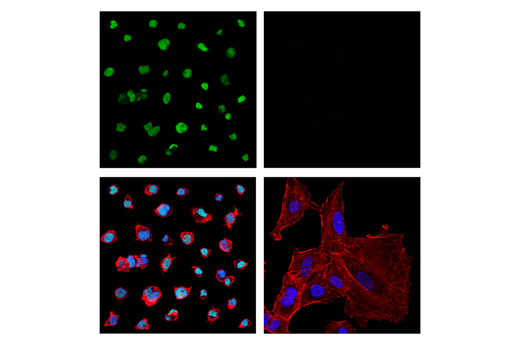
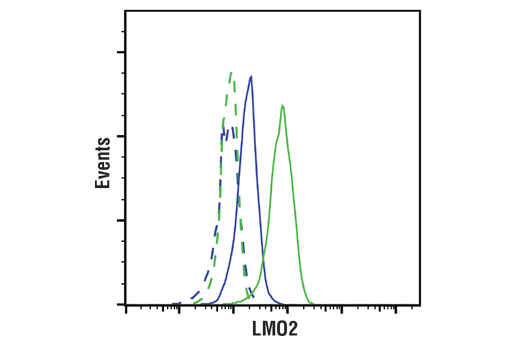
WB, IF-IC, FC-FP, ChIP, ChIP-seq
H
Endogenous
18
Rabbit IgG
#P25791
4005
Product Information
Product Usage Information
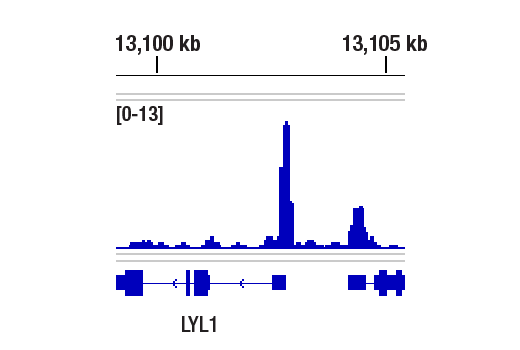
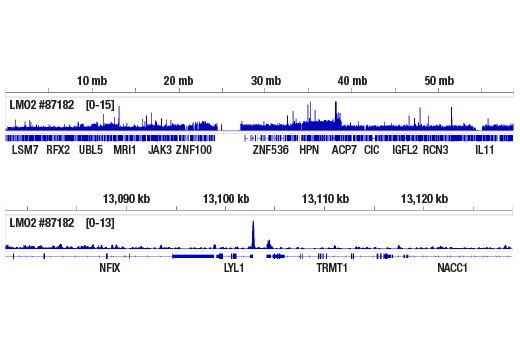
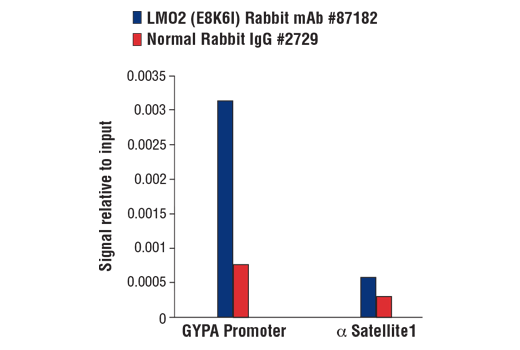
For optimal ChIP and ChIP-seq results, use 5 μL of antibody and 10 μg of chromatin (approximately 4 x 10^6 cells) per IP. This antibody has been validated using SimpleChIP® Enzymatic Chromatin IP Kits.
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) | 1:1600 - 1:6400 |
| Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized) | 1:400 - 1:1600 |
| Chromatin IP | 1:100 |
| Chromatin IP-seq | 1:100 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human
Source / Purification
Monoclonal antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues near the amino terminus of human LMO2 protein.
Background
LIM-domain-only protein 2 (LMO2) is a transcriptional regulator that was first identified as a proto-oncogene activated by chromosomal translocations in T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (T-ALL) (1). Since then, LMO2 has been found to be a master regulator essential for erythroid development, as evidenced by homozygous LMO2 knockouts resulting in embryonic lethality in mice (2). LMO2 is an intrinsically unstructured protein that does not bind DNA directly, but rather acts as a scaffolding protein that recruits various transcription factors via its tandem cysteine-rich LIM domains to form a multi-protein DNA binding complex (3,4). The LMO2 complex plays a major role in hematopoiesis and was originally shown to consist of the transcription factors TAL1, E47, and GATA-1 in erythroid lineage cells, but variations of this complex may contain alternate transcription factors including LYL1, TAL2, GATA-2, and GATA-3 (5-9). The LMO2 complex also requires interaction with LIM-domain binding protein 1 (LDB1), which is necessary for LMO2 protein stability (10-11). In addition to hematopoietic tissue, LMO2 is also expressed in embryonic brain tissue, where it associates with BEX2 and the transcription factor NSCL-2 (12). Aberrant LMO2 expression is observed in several types of hematopoietic cancers, including large diffuse B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), B-cell acute leukemia, (B-ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and T-ALL (13-16). LMO2-mediated T-ALL is primarily caused by the translocation t(11;14)(p13;q11) with the TCRD/A gene from chromosome 14q11, or the t(7;11)(q35;p13) translocation involving TCRB from 7q35 (1). In addition to hematopoietic cancers, overexpression of LMO2 in prostate stromal cells also facilitates prostate cancer progression by inducing expression of Interleukin-11 (IL-11), which stimulates STAT3 signaling in these cells (17).
- Boehm, T. et al. (1991) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88, 4367-71.
- Warren, A.J. et al. (1994) Cell 78, 45-57.
- Chambers, J. and Rabbitts, T.H. (2015) Open Biol 5, 150062.
- Lécuyer, E. et al. (2007) J Biol Chem 282, 33649-58.
- Valge-Archer, V.E. et al. (1994) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91, 8617-21.
- Wadman, I. et al. (1994) EMBO J 13, 4831-9.
- Wadman, I.A. et al. (1997) EMBO J 16, 3145-57.
- Osada, H. et al. (1995) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92, 9585-9.
- Ono, Y. et al. (1998) Mol Cell Biol 18, 6939-50.
- Agulnick, A.D. et al. (1996) Nature 384, 270-2.
- Layer, J.H. et al. (2016) Mol Cell Biol 36, 488-506.
- Han, C. et al. (2005) Nucleic Acids Res 33, 6555-65.
- Natkunam, Y. et al. (2007) Blood 109, 1636-42.
- de Boer, J. et al. (2011) Leukemia 25, 321-30.
- Atay, M.H. et al. (2013) Histopathology 63, 293-4.
- Patel, J.L. et al. (2014) Histopathology 64, 226-33.
- Jiang, C.Y. et al. (2016) Oncotarget 7, 26247-58.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v BSA, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IF-IC: Immunofluorescence (Immunocytochemistry) FC-FP: Flow Cytometry (Fixed/Permeabilized) ChIP: Chromatin IP ChIP-seq: Chromatin IP-seq
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.