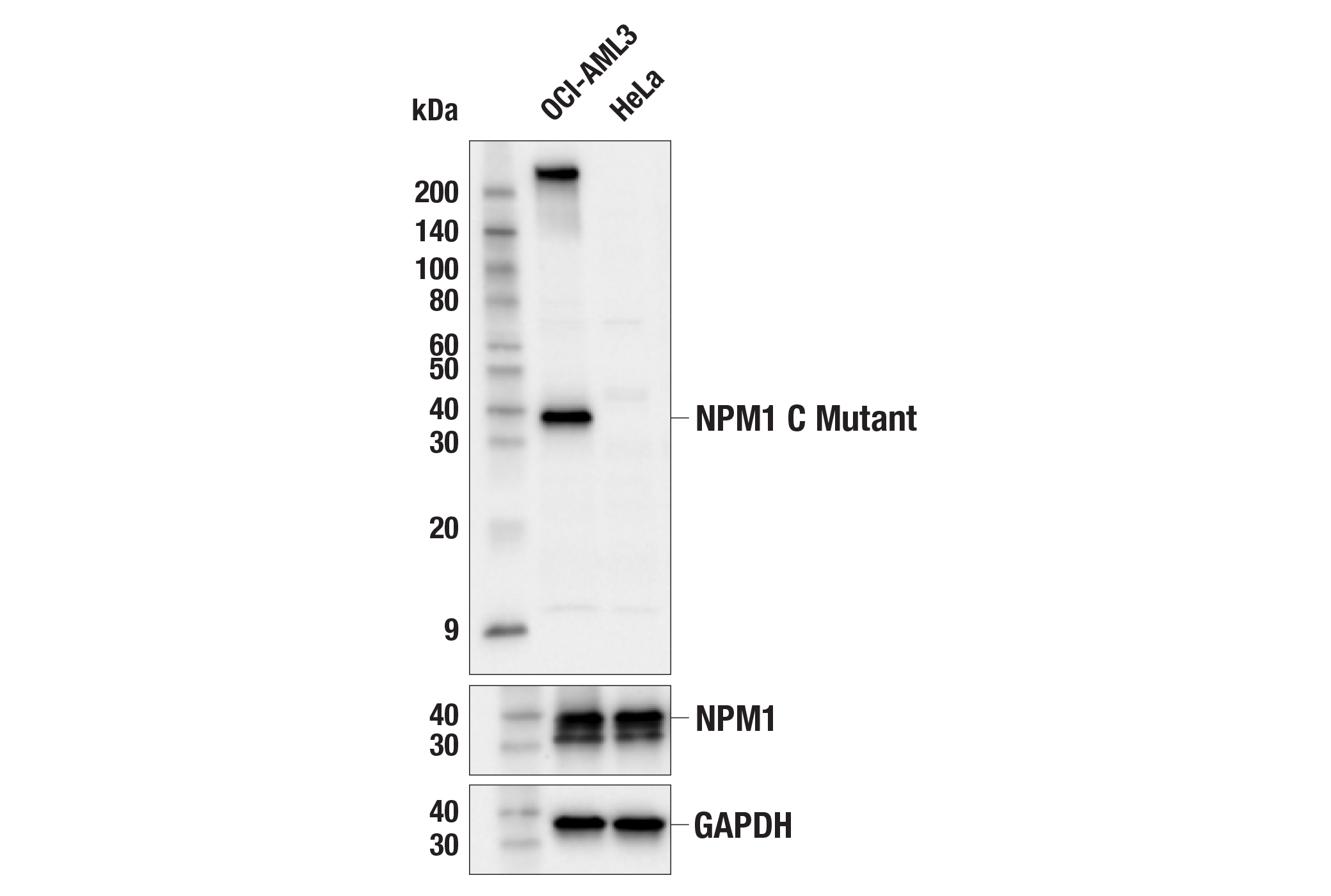
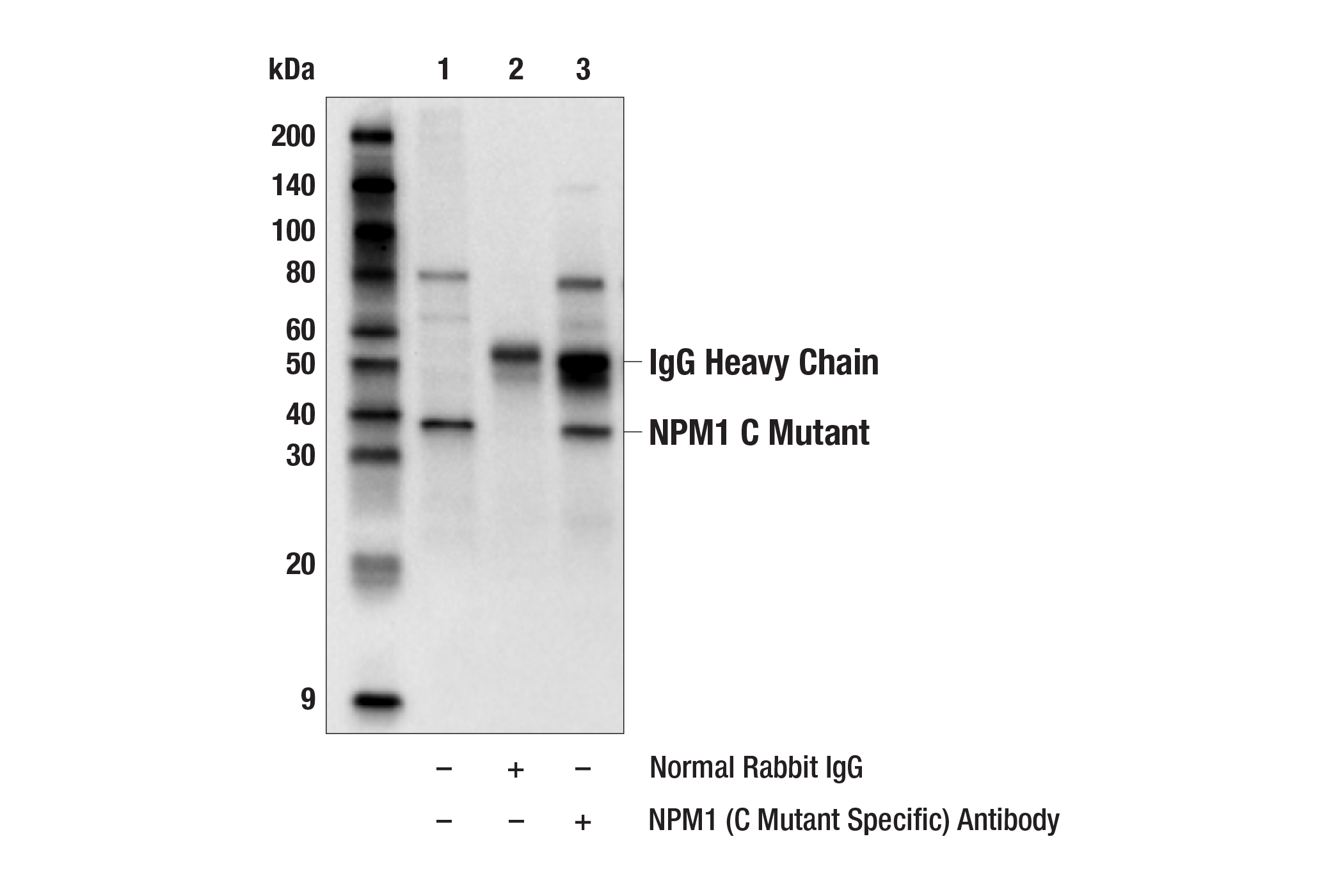
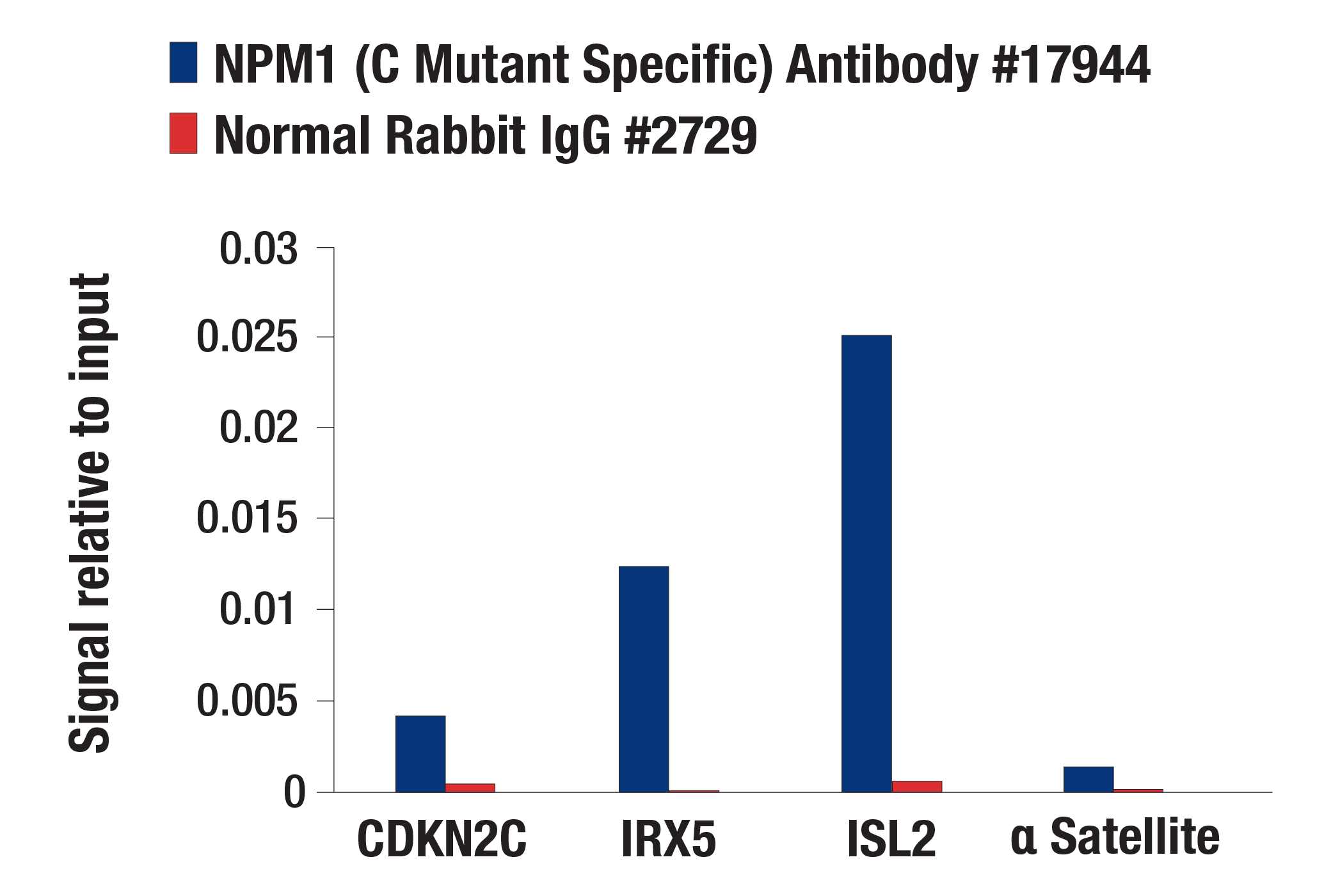
WB, IP, ChIP
H
Endogenous
38
Rabbit
#P06748
4869
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:50 |
| Chromatin IP | 1:50 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human
Source / Purification
Polyclonal antibodies are produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues near the mutated carboxy terminus of human NPM1 C mutant protein. Antibodies are purified by peptide affinity chromatography.
Background
Nucleophosmin (NPM1; also known as NPM, B23, numatrin, or NO38) is an abundant phosphoprotein primarily found in nucleoli. It has been implicated in several distinct cellular functions, including assembly and transport of ribosomes, cytoplasmic/nuclear trafficking, regulation of DNA polymerase α activity, centrosome duplication, and molecular chaperoning activities (1,2). The NPM1 gene is also known for its fusion with the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) receptor tyrosine kinase. The NPM1 portion contributes to transformation by providing a dimerization domain, which results in activation of the fused kinase (3,4). NPM1 is also the most frequently mutated gene in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and accounts for nearly 30% of all cases (5). These AML subtypes, classified as NPM1-mutated AML, are characterized by mutations in NPM1’s C-terminus that disrupt its nucleolar localization sequence and cause mislocalization from the nucleolus to the cytoplasm (6). This cytoplasmic form of NPM1, commonly referred to as NPM1c, is exclusive to myeloid malignancies and is not found in other forms of cancer (7). These mutations are always heterozygous, and NPM1c functions in a dominant negative fashion by dimerizing with wild-type NPM1 and recruiting it to the cytoplasm (6,8). Interestingly, NPM1 mutations alone are not sufficient to drive leukemogenesis, and further research is required to fully elucidate the impact of these mutations on disease progression (9).
- Okuda, M. et al. (2000) Cell 103, 127-40.
- Takemura, M. et al. (1999) J Biochem 125, 904-9.
- Morris, S.W. et al. (1994) Science 263, 1281-4.
- Bischof, D. et al. (1997) Mol Cell Biol 17, 2312-25.
- Falini, B. et al. (2005) N Engl J Med 352, 254-66.
- Falini, B. et al. (2006) Blood 107, 4514-23.
- Zarka, J. et al. (2020) Genes (Basel) 11, .
- den Besten, W. et al. (2005) Cell Cycle 4, 1593-8.
- Vassiliou, G.S. et al. (2011) Nat Genet 43, 470-5.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v nonfat dry milk, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation ChIP: Chromatin IP
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.