WB, IP
H M R Mk
Endogenous
57
Rabbit
#P08670
7431
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:50 |
Storage
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey
Source / Purification
Polyclonal antibodies are produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser39 of human vimentin protein. Antibodies are purified by protein A and peptide affinity chromatography.
Background
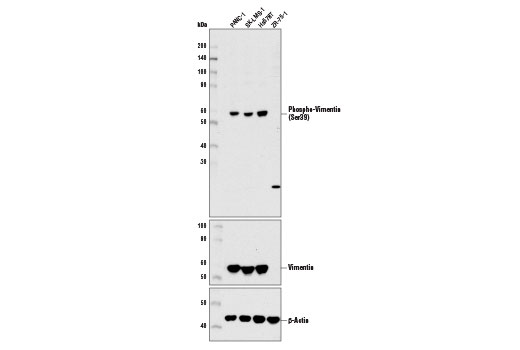
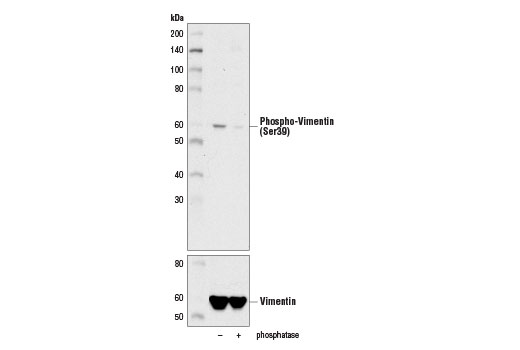
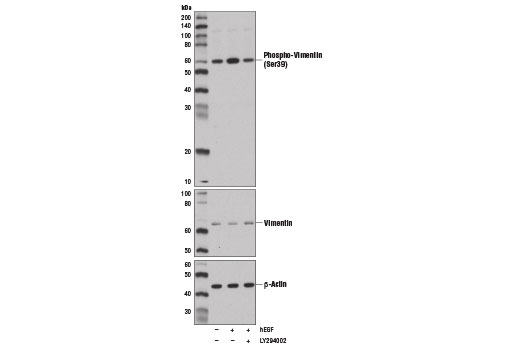
The cytoskeleton consists of three types of cytosolic fibers: microfilaments (actin filaments), intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Major types of intermediate filaments are distinguished by their cell-specific expression: cytokeratins (epithelial cells), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (glial cells), desmin (skeletal, visceral, and certain vascular smooth muscle cells), vimentin (mesenchyme origin), and neurofilaments (neurons). GFAP and vimentin form intermediate filaments in astroglial cells and modulate their motility and shape (1). In particular, vimentin filaments are present at early developmental stages, while GFAP filaments are characteristic of differentiated and mature brain astrocytes. Thus, GFAP is commonly used as a marker for intracranial and intraspinal tumors arising from astrocytes (2). Research studies have shown that vimentin is present in sarcomas, but not carcinomas, and its expression is examined in conjunction with that of other markers to distinguish between the two (3). Vimentin's dynamic structural changes and spatial re-organization in response to extracellular stimuli help to coordinate various signaling pathways (4). Phosphorylation of vimentin at Ser56 in smooth muscle cells regulates the structural arrangement of vimentin filaments in response to serotonin (5,6). Remodeling of vimentin and other intermediate filaments is important during lymphocyte adhesion and migration through the endothelium (7).
During mitosis, CDK1 phosphorylates vimentin at Ser56. This phosphorylation provides a PLK binding site for vimentin-PLK interaction. PLK further phosphorylates vimentin at Ser83, which might serve as memory phosphorylation site and play a regulatory role in vimentin filament disassembly (8,9). Additionally, studies using various soft-tissue sarcoma cells have shown that phosphorylation of vimentin at Ser39 by Akt1 enhances cell migration and survival, suggesting that vimentin could be a potential target for soft-tissue sarcoma targeted therapy (10,11).
- Eng, L.F. et al. (2000) Neurochem Res 25, 1439-51.
- Goebel, H.H. et al. (1987) Acta Histochem Suppl 34, 81-93.
- Leader, M. et al. (1987) Histopathology 11, 63-72.
- Helfand, B.T. et al. (2004) J Cell Sci 117, 133-41.
- Tang, D.D. et al. (2005) Biochem J 388, 773-83.
- Fomina, I.G. et al. (1990) Klin Med (Mosk) 68, 125-7.
- Nieminen, M. et al. (2006) Nat Cell Biol 8, 156-62.
- Yamaguchi, T. et al. (2005) J Cell Biol 171, 431-6.
- Oguri, T. et al. (2006) Genes Cells 11, 531-40.
- Zhu, Q.S. et al. (2011) Oncogene 30, 457-70.
- Xue, G. and Hemmings, B.A. (2013) J Natl Cancer Inst 105, 393-404.
Species Reactivity
Species reactivity is determined by testing in at least one approved application (e.g., western blot).
Western Blot Buffer
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 5% w/v nonfat dry milk, 1X TBS, 0.1% Tween® 20 at 4°C with gentle shaking, overnight.
Applications Key
WB: Western Blotting IP: Immunoprecipitation
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.