Cancer Immunology Research
Immune Checkpoint Control
The healthy immune system employs a series of checkpoints, which are in-built control mechanisms, in order to maintain self-tolerance or prevent collateral tissue damage during an immune response. Protein expression involved at immune checkpoints is often dysregulated in cancer cells as a means to evade immune detection.
Intense research and drug development for cancer treatment focuses on activating anti-tumor immunity by modulating immune checkpoint proteins. Therefore, in order to understand the complex tissue microenvironment under both physiological and pathological conditions such as cancer, profiling immune checkpoint proteins and phenotypic markers is important. This can be reliably achieved by through immunohistochemistry (IHC) using validated antibodies.
CST offers human-reactive and mouse-reactive IHC validated antibodies that enable investigators to get more information about biomarker expression, localization, interaction and disease context.
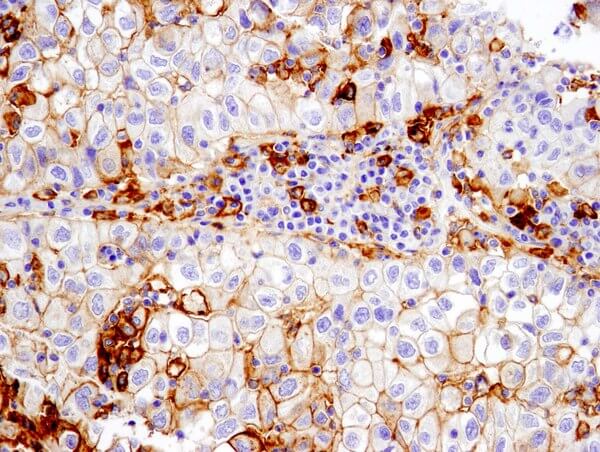
PD-L1 (E1L3N®) XP® Rabbit mAb #13684: IHC analysis of paraffin-embedded human non-small cell lung carcinoma using #13684 performed on the Leica® Bond™ Rx.
Adoptive Cell Therapy
Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapy has recently shown promising results as a cancer immunotherapy:
- T cells are collected from a patient, engineered to express a specific chimeric antigen receptor that is specific for the patient’s cancer cells, and re-infused.
- CAR-T cells can locate and eradicate tumor cells based on the expression of the specific tumor-associated antigen on the cell surface of the tumor.
In order to realize the remarkable power of adoptive cell therapy, visualizing your modified T cells of interest is important. Several modalities, including immunohistochemistry (IHC), can be utilized to confirm the characteristics and spatial context of the T cell population in your studies.
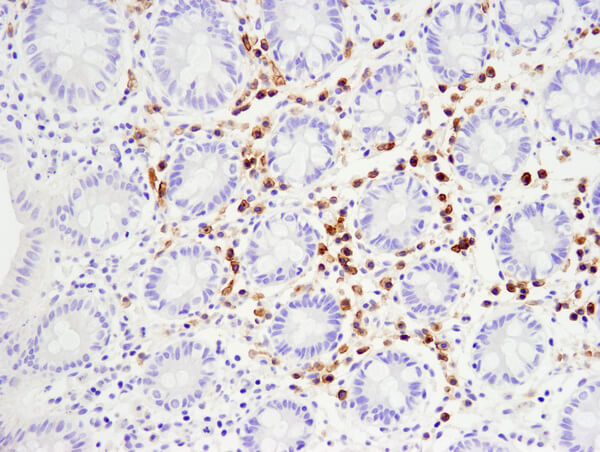
TNFRSF17/BCMA (E6D7B) Rabbit mAb #88183: IHC analysis of paraffin-embedded human normal colon using #88183.
Immunosuppression in the Tumor Microenvironment
The validation of immune checkpoint inhibitors as immunotherapeutic agents for a variety of cancers has revolutionized the field of cancer immunology therapy. An advanced understanding of the immune regulatory context of the tumor microenvironment (TME) is required to harness the power of the anti-tumor immune response.
Spatial context, co-localization, and proximity of multiple biomarkers is critical when cataloging subsets of immune infiltrate and cancer cells and their interactions in the TME. Therefore, immunohistochemistry (IHC) and multiplex IHC (mIHC), which enables detection of 6 or more proteins/biomarkers in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples, is a valuable tool for immuno-oncology.
Using validated antibodies against relevant targets is crucial in order to obtain results confidently. CST® antibodies are validated for IHC by our support scientists to better understand biomarker expression, as well as localization and interactions of cells in a specific microenvironment.
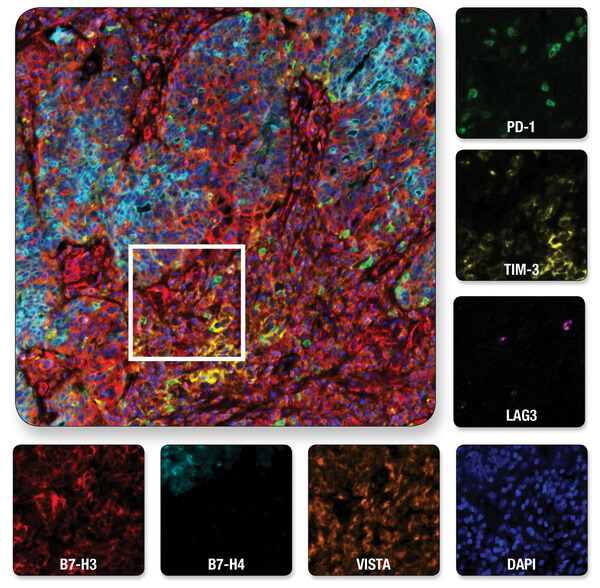
Multiplexed IHC analysis of ovarian serous carcinoma tissue probed with a 6-plex panel for co-inhibitory immune checkpoint proteins, plus DAPI to label nuclei. Multiplexed image of all seven channels (upper left) is shown with a region of interest (white box in upper left) from which the individual channels are displayed.
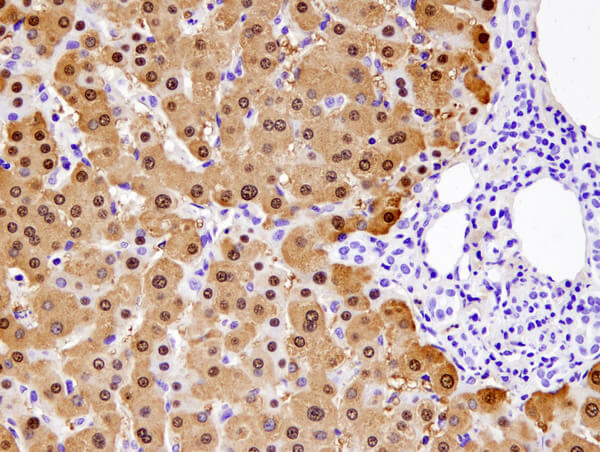
Arginase-1 (D4E3M™) XP® Rabbit mAb #93668: IHC analysis of paraffin-embedded normal human liver using #93668.