PTMScan® Glycosylation
Glycosylation, the covalent addition carbohydrate groups to proteins, is a common post-translational modification that affects protein structure, stability, and signaling. Glycosylation is of particular importance on membrane and secreted proteins, including immunoglobulins. N-linked glycosylation involves addition of the glycan groups to asparagine residues on proteins, with these glycans often containing a terminal sialic acid group. After protease digestion, sialic acid-containing glycopeptides can be enriched using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC), in which the positively charged metal ion will interact with the negatively charged sialic acid group.
Traditionally, mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of glycosylation has been focused either on identification of the peptides that were glycosylated or on the structure of the glycan itself, but not resolution of both peptide sequence and glycan structure at the same time. PTMScan® Glycosylation profiling provides both the peptide sequence and the glycan structure at the same time. This allows identification and quantification of hundreds to thousands of glycosylated peptides with the structure of the glycan group included. Using PTMScan® Glycosylation analysis the landscape of glycosylation in serum or media samples can be profiled, and changes in that landscape quantified to find glycosylation events regulated by a particular treatment.
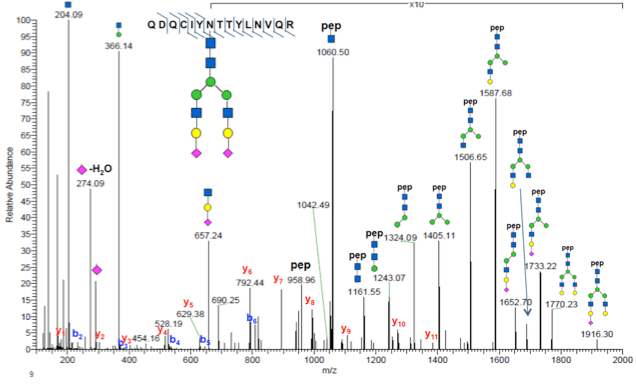
MS/MS spectrum of a glycopeptide identified using PTMScan Glycosylation profiling. Both the peptide sequence and the structure of the glycan are determined from the same spectrum. Fragment ions corresponding to peptide backbone (b and y ions) and glycan groups (structures of individual sugar units) are indicated.